- Home
- Periodontics
TOP Quality
dental
services
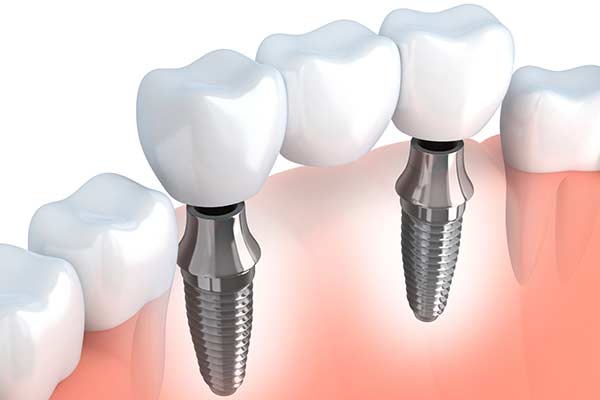

Dental Implants
Dental implants are used to replace missing teeth. The implant is made from a titanium post that’s...
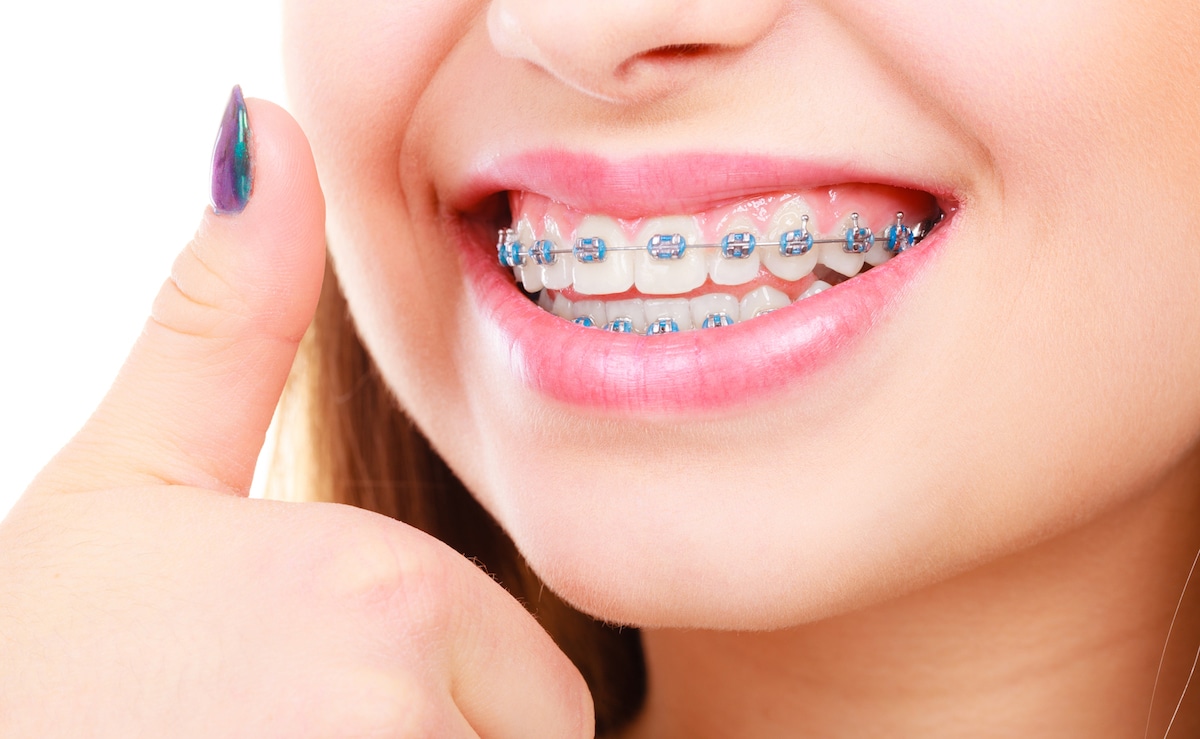


Orthodontic Treatment
Mal-aligned teeth can leave you feeling less than happy about your smile. Enhance your smile by stra...
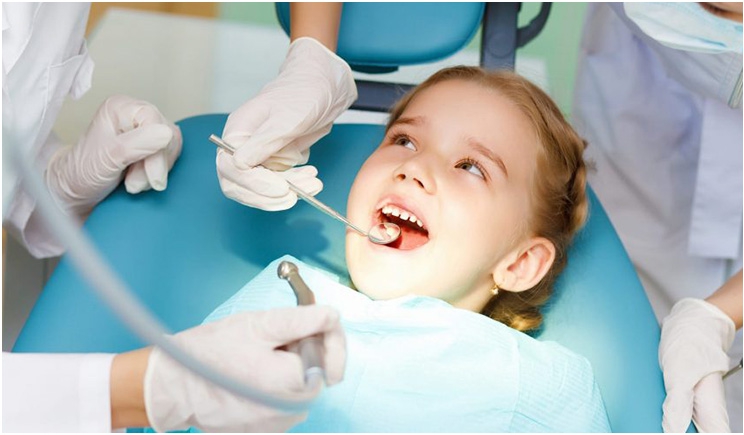

Pediatric Dentistry
The dentistry for children is all about having the best experience at the dentist, our team is commi...
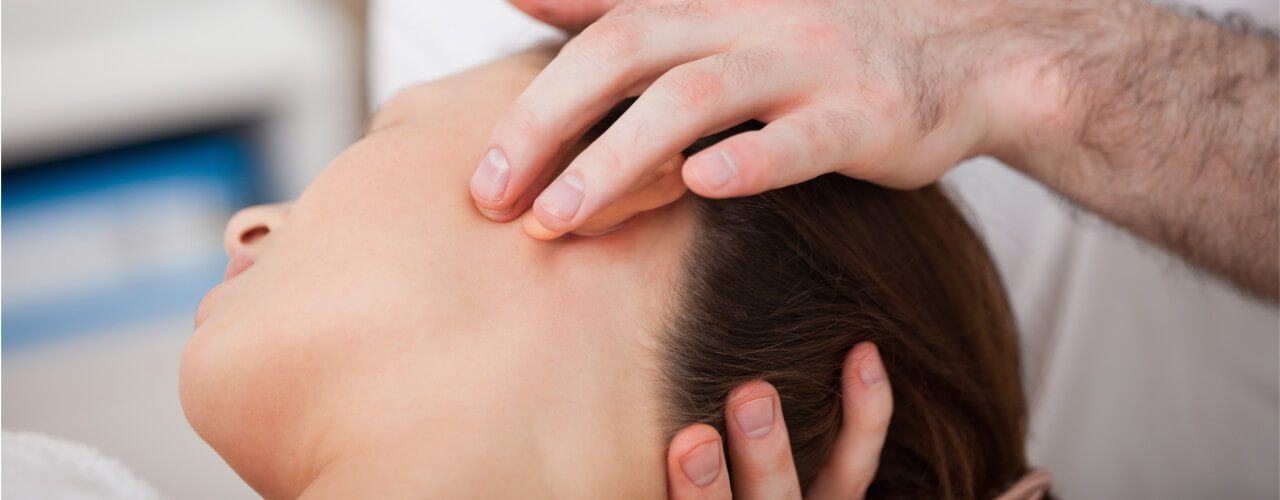

TMJ Treatment
Temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) occurs when you have pain and dysfunction in the joints or in...
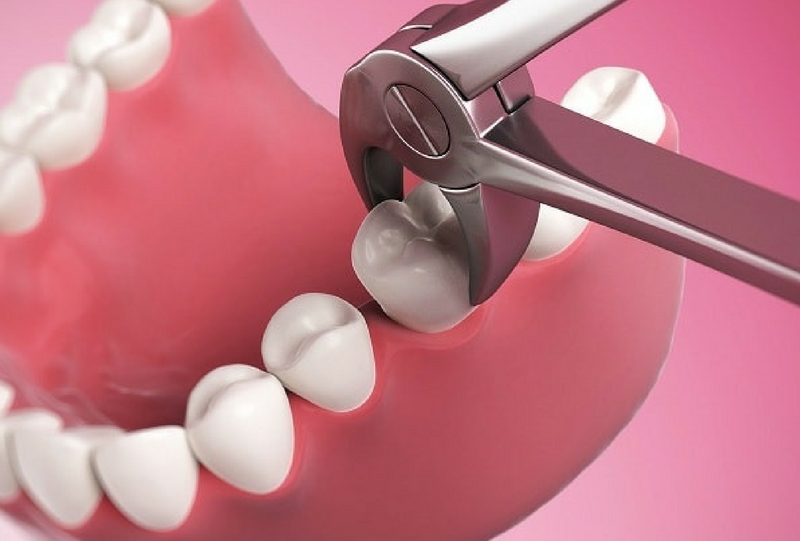

Tooth Extraction
Teeth often need to be removed when they’re so damaged or decayed that they can’t be saved with ...
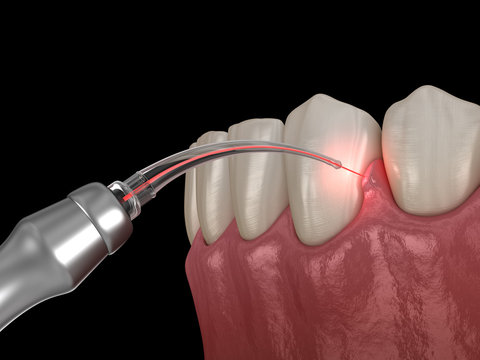

Periodontics
Gum disease (periodontal disease), occurs when gums have a bacterial infection. If the infection goe...
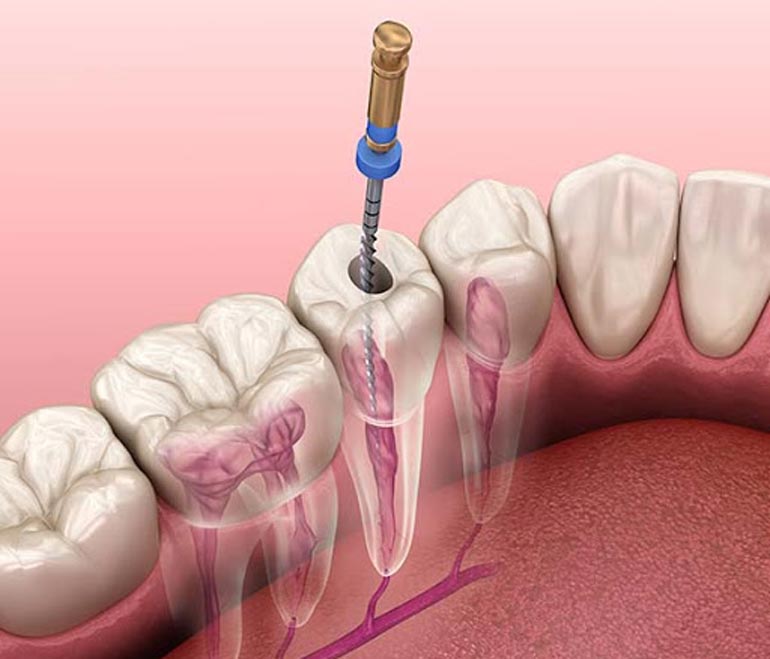
Endodontics
Painful, injured and abscessed teeth are routinely managed by our dentists, but sometimes the proble...
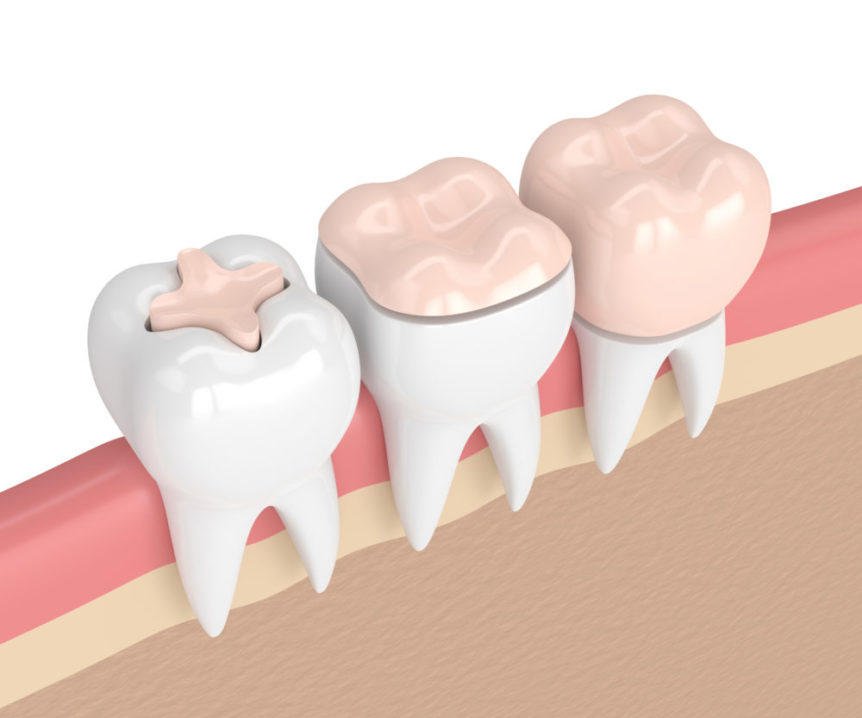

Porcelain Inlays/Onlays
Our dental office offers two specific types of dental fillings: porcelain inlays and porcelain onlay...
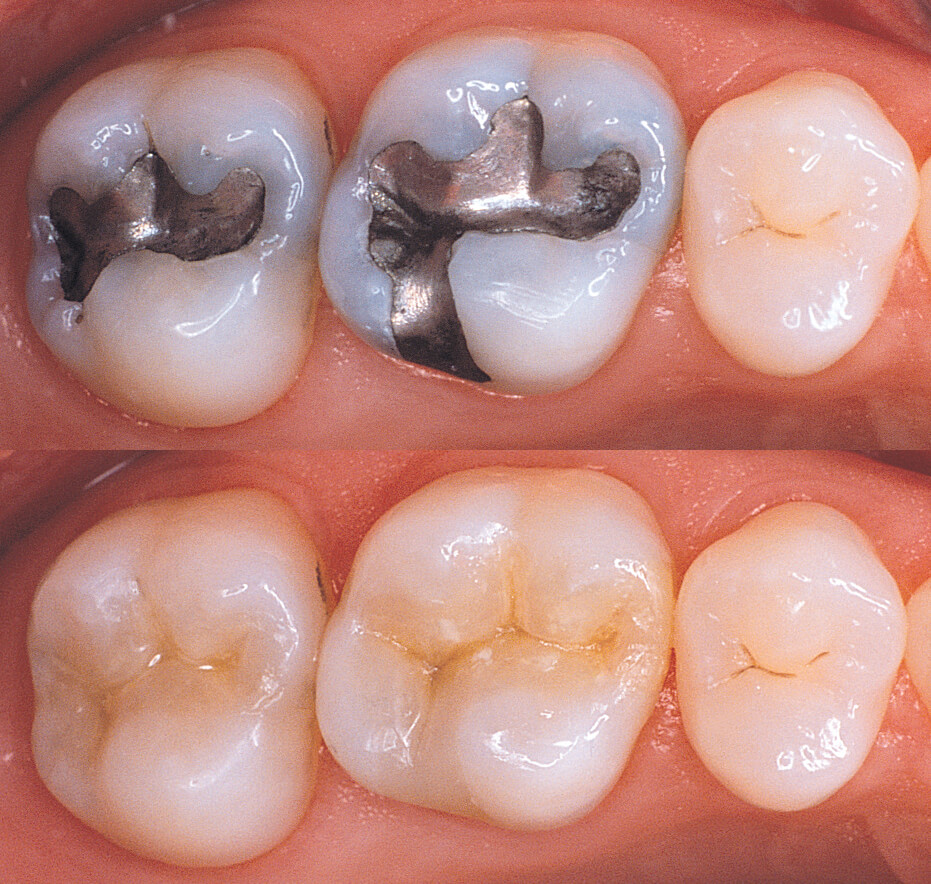

Tooth Colored Fillings
Made from a plastic dental resin, we match the shade of your tooth’s natural enamel. This is espec...
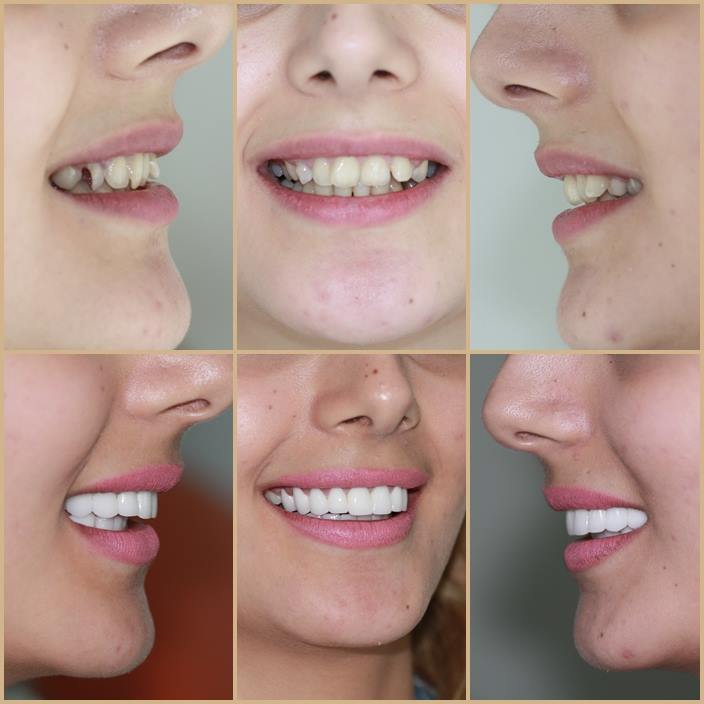

Smile Makeovers
A full mouth reconstruction, more commonly known as a smile makeover, is a series of procedures aime...
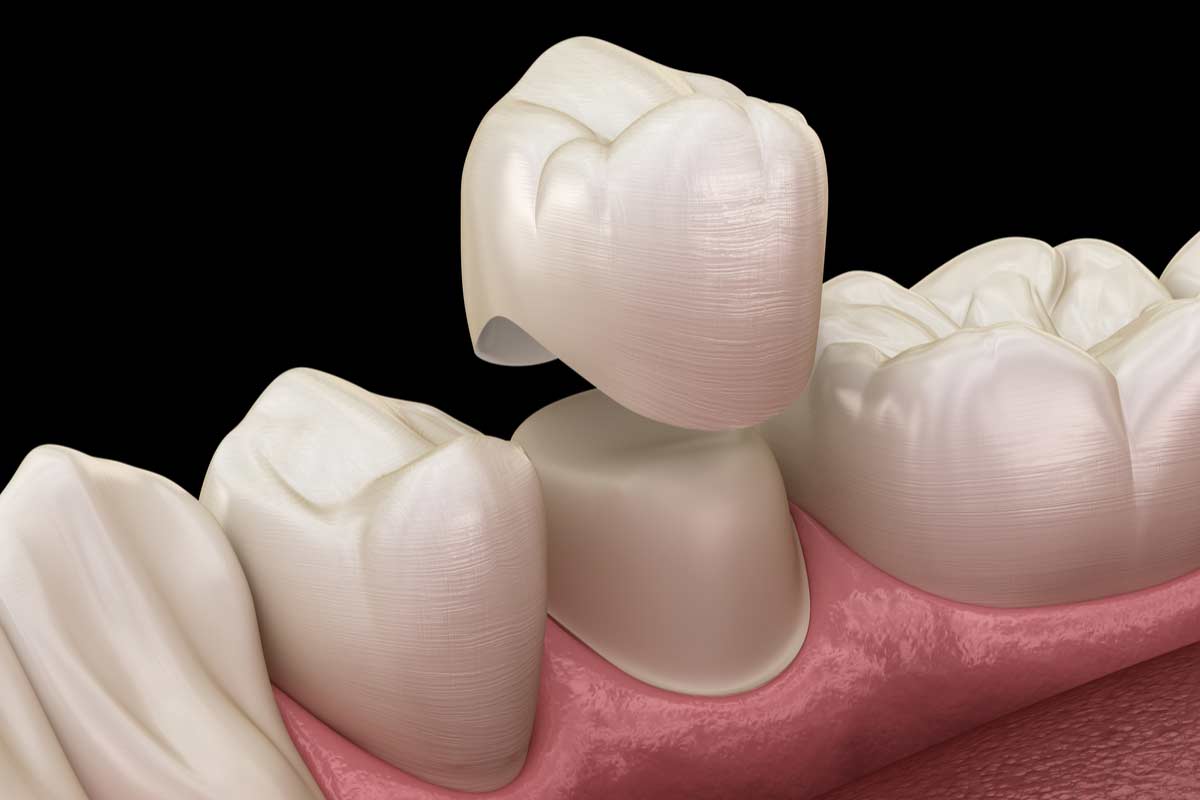

Dental Crowns
Dental crowns are used to address problems such as broken or cracked teeth or tooth decay. A permane...
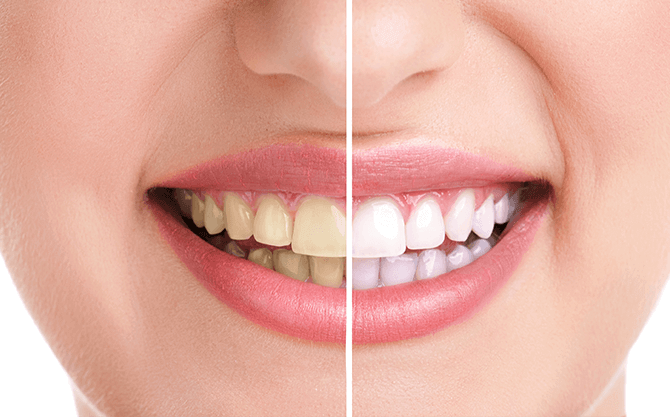


Teeth Whitening
Teeth often get discolored from years of drinking coffee and tea, because colored pigments in these ...
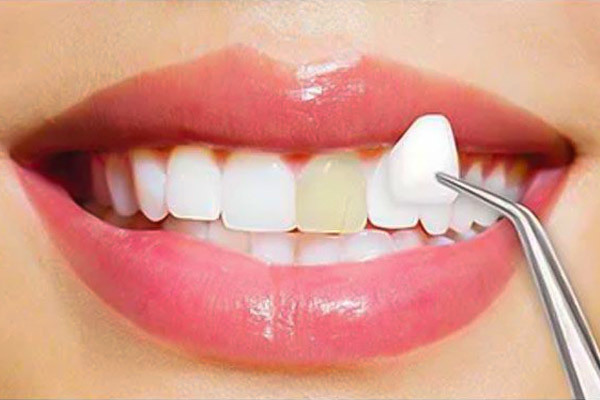

Dental Veneers
Dental veneers are thin covers that are attached to the outside of teeth to hide imperfections. Vene...
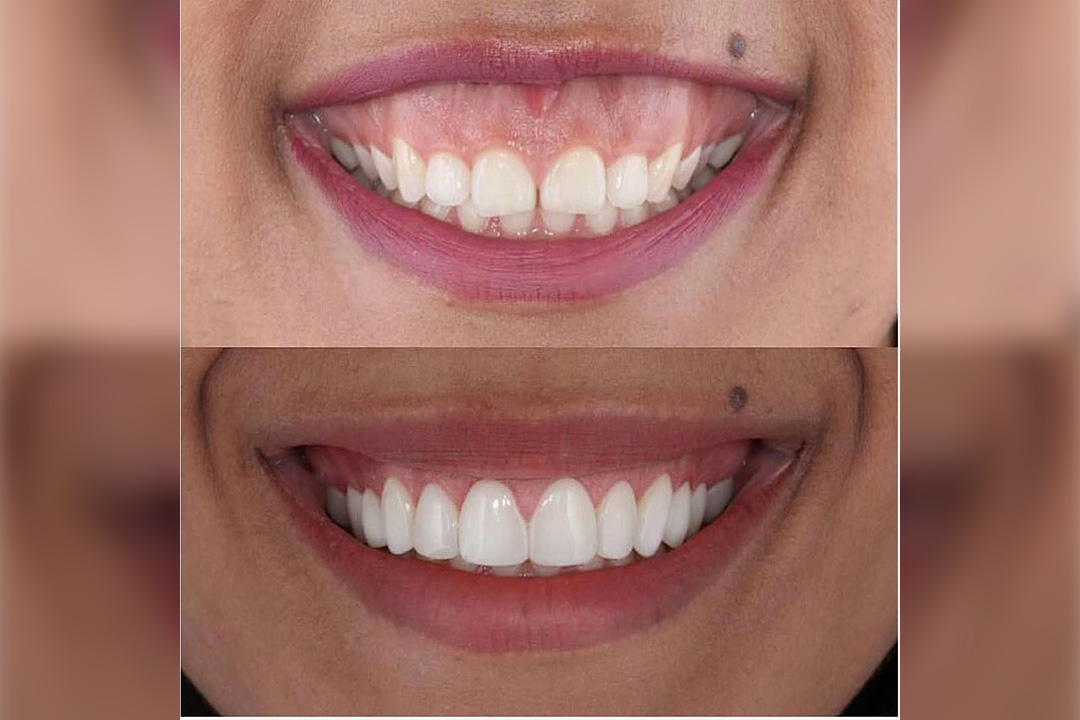

Gummy Smile Corrections
Gummy smile refers to the condition where the gum is very exposed when a person smile. We can treat ...
New Cairo
Bld.224 Behind Dusit Thani Hotel - 90th Axis - Cairo, Egypt
(+2) 01027050446
(+2) 0102705 0447
Powered By Magints


Gum disease (periodontal disease), occurs when gums have a bacterial infection. If the infection goes untreated, it damages the gum tissue and destroys the fibers and bones that hold teeth in your mouth. As a result, gum disease can lead to loss of teeth.
Periodontal disease is usually caused by poor oral hygiene. The mouth is normally full of bacteria, which mix with sugar and starch to form a plaque that sticks to your teeth. If the plaque isn’t removed, it turns into a hard substance called tartar. When plaque and tartar aren’t removed, bacteria have plenty of time to cause inflammation and infection. Symptoms indicating you may have gum disease include; bad breath, sensitive teeth, bleeding gums, red or swollen gums, receding gums and loose teeth. When gum inflammation, or gingivitis, is caught early, it may be treated with a dental cleaning. In some cases, the dentist may prescribe an antibiotic to eliminate the infection. However, untreated gingivitis progresses to become periodontitis. In this condition, inflammation spreads around the tooth and under the gums, allowing bacteria and toxins to get into the bone.
Periodontitis may be treated with nonsurgical procedures called scaling and root planning, which gets rid of all the plaque and tartar on the surface of the tooth and its root. But when periodontitis is more advanced because inflammation and damage to bone is too severe, then periodontal surgery is needed to save the tooth and surrounding structures.
We have extensive experience performing different types of traditional periodontal surgery. Some periodontal surgery is done in healthy gums, such as a gingivectomy to remove excess gum tissue, and a gingivoplasty to reshape the gums.
One of the most common procedures for treating periodontitis is called flap surgery. During this procedure, gum tissue is temporarily folded away from teeth to allow plaque, tartar, bacteria, and damaged tissue to be cleaned away. A bone graft may also be performed to regenerate and strengthen damaged bone.